Research Areas 研究内容
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Overview
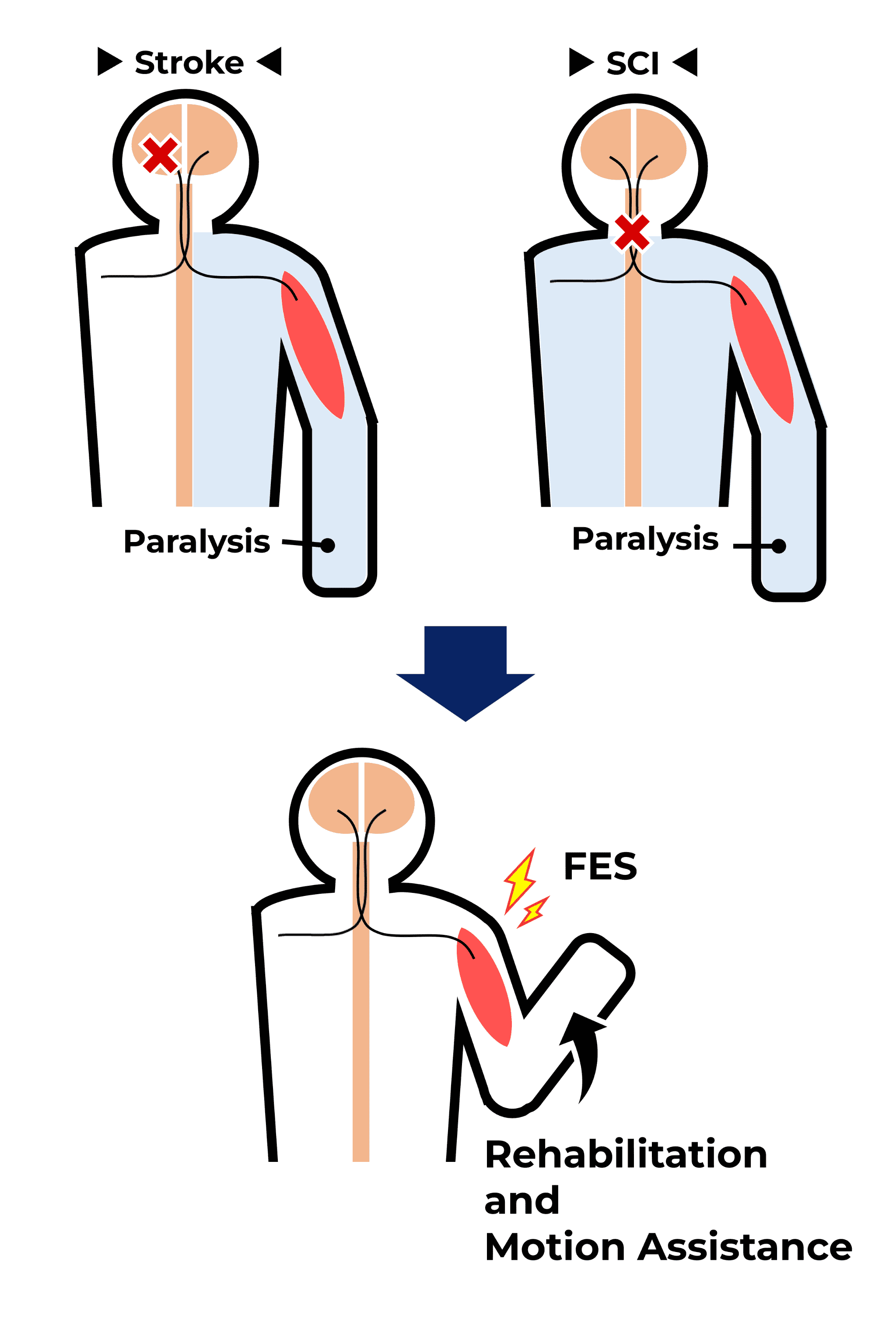
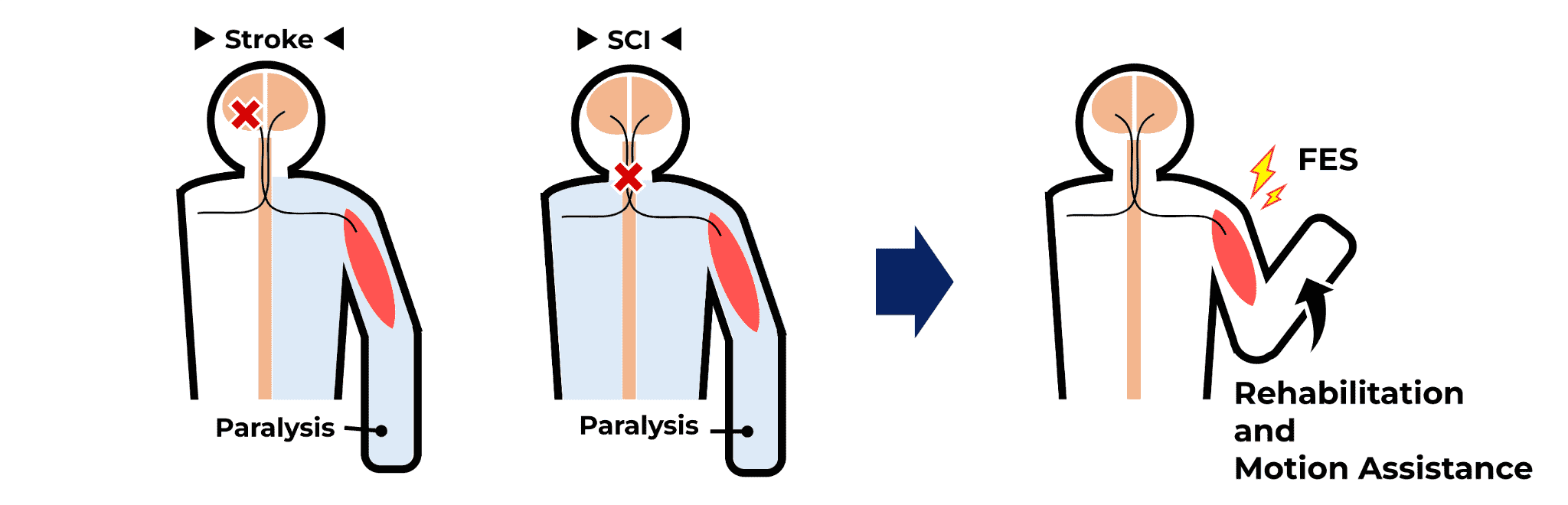
When we move our bodies, motor command from the brain are transmitted to muscles as electrical signals. In cases of spinal cord injuries or cerebrovascular diseases such as stroke, paralysis of motor or sensory functions is caused because of problems in the pathways of these electrical signals.
However, when the motor nerves and muscles responsible for movement are normal, external electrical stimulation can cause the muscles to contract and produce movement. This method, which uses external electrical stimulation to assist or restore movement, is called functional electrical stimulation (FES).
Focus Area 1: Error Feedback Learning Controller
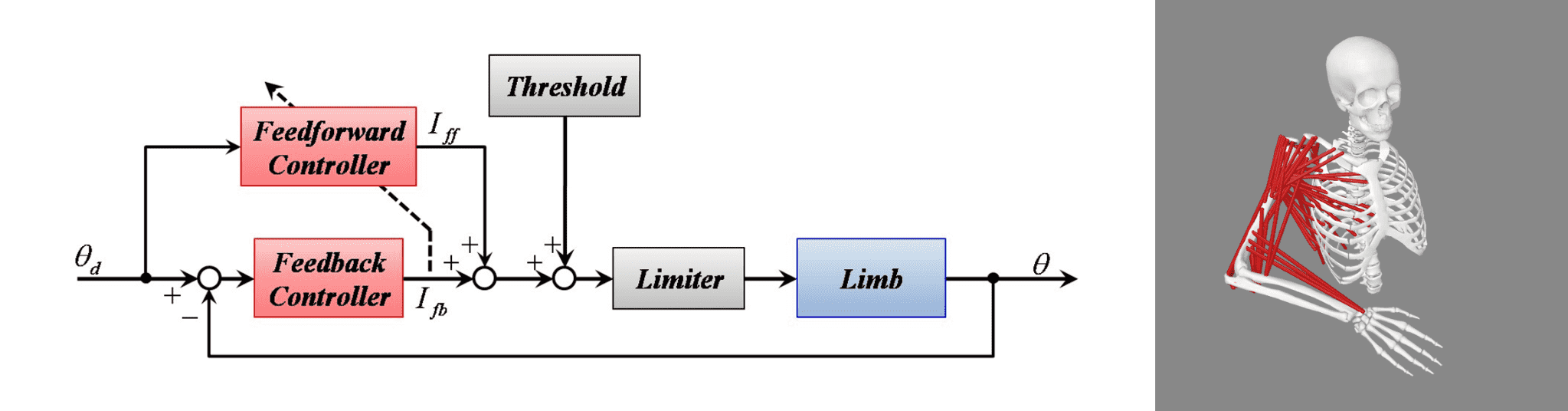
The musculoskeletal system has nonlinear characteristics and is affected by muscle fatigue and individual differences, making it a very difficult control target. In Watanabe Laboratory, accurate FES control method that can accommodate these nonlinearities and individual differences is developing.
One such method is an FES controller that applies feedback error learning. This method uses artificial neural network (ANN) as the feedforward controller, which learns the characteristics of the target during control, This make it possible to respond to nonlinearity and individual differences.
Recently, the method to reduce the number of preliminary measurements required to reduce the burden on patients is developing with using musculoskeletal models for pre-training ANNs.
Focus Area 2: Foot-Powered Wheelchair Rehabilitation System
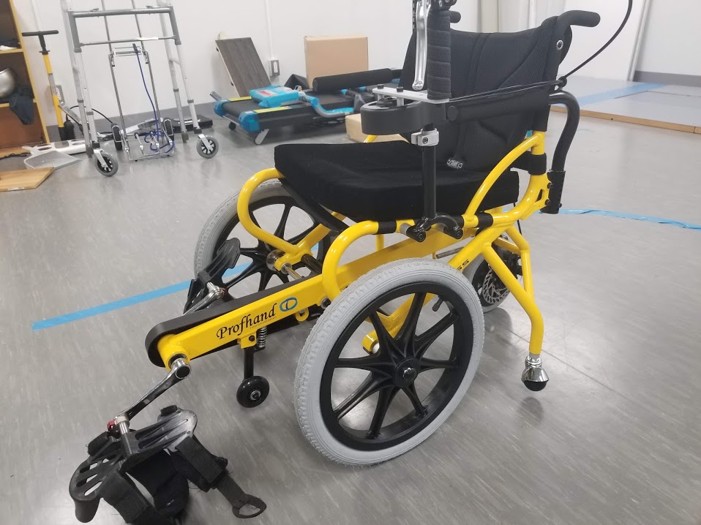

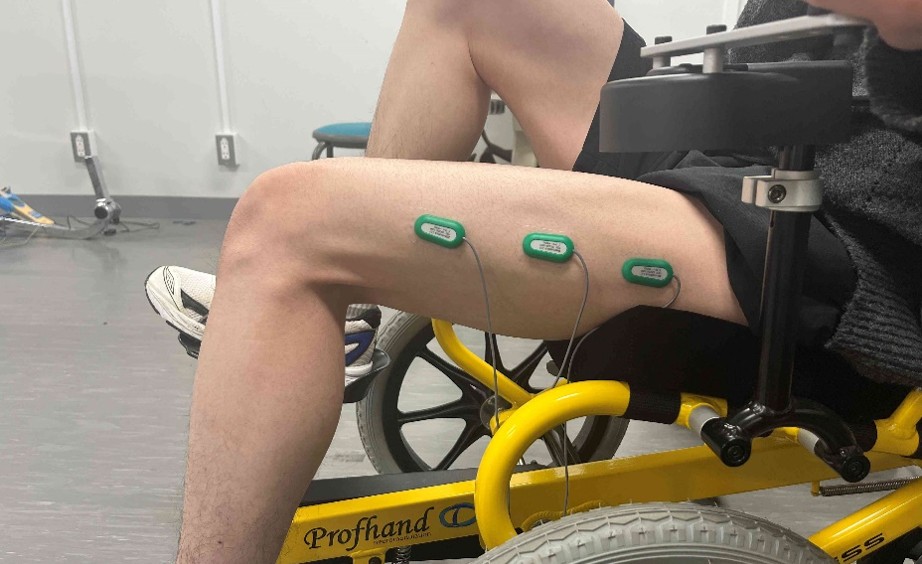
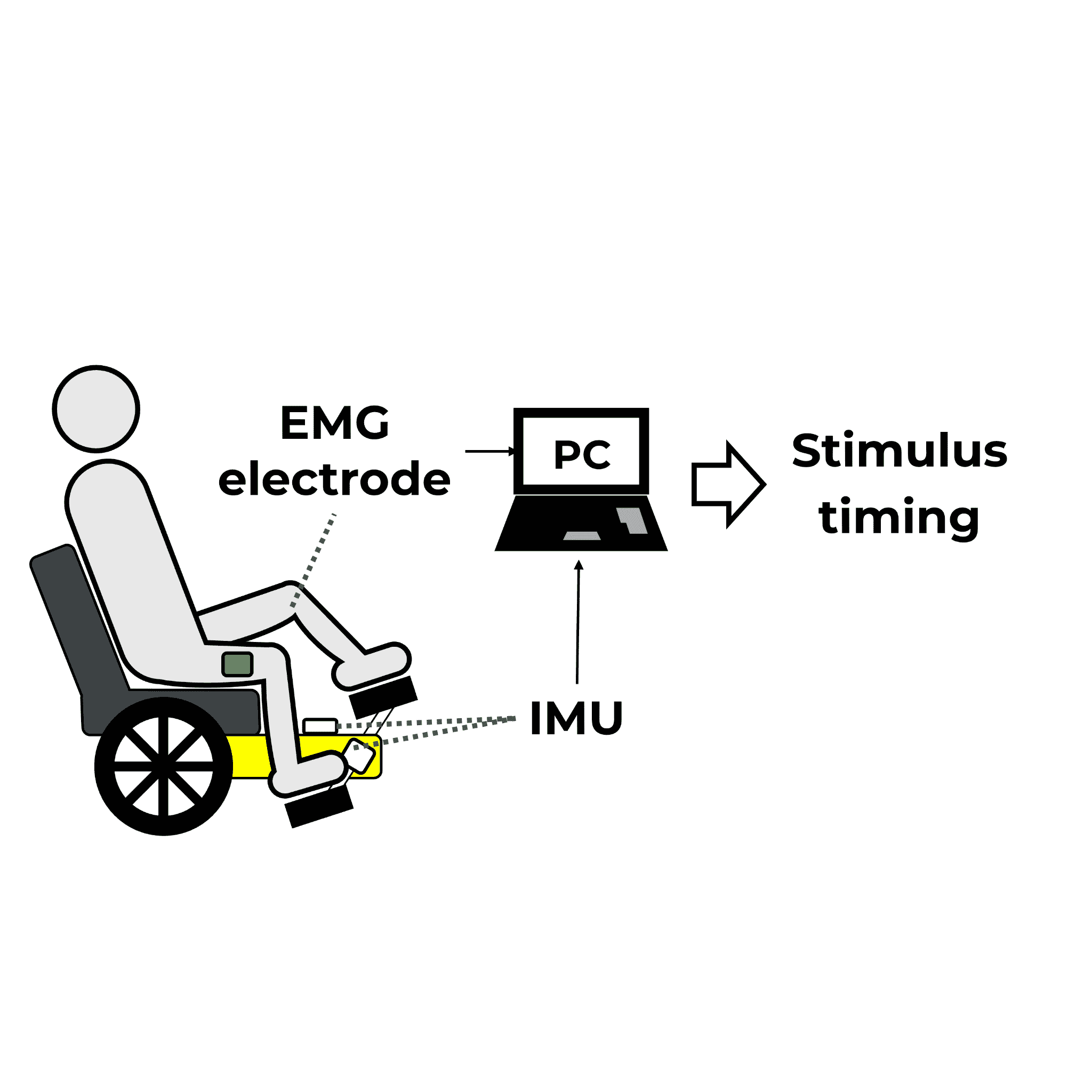

When using FES for paralyzed limbs, it is necessary to stimulate with the appropriate intensity and timing according to the movement. In addition, it has been found that combining FES with the patient's voluntary movement enhances rehabilitation effects, so the use of FES according to the movement is important.
In Watanabe Laboratory, to combine FES with foot-powered wheelchairs is worked to develop practical applications for rehabilitation and mobility. Foot-powered wheelchair is propelled by pedaling with the feet, similar to bicycles. They enable elderly people and patients with hemiplegia who have difficulty walking independently to move around by operating the wheelchair with their own feet. They are expected to be effective in preventing disuse syndrome, such as muscle weakness and joint stiffness.
We have previously proposed a method for determining the timing of electrical stimulation based on crank angle. Recently, we have focused on the fact that the appropriate stimulation timing varies depending on speed and individual differences and working toward practical application.
Gait Assessment
Overview
Gait assessment is crucial for understanding movement disorders and evaluating the effectiveness of therapies. Our laboratory is engaged in both the development of tools for movement monitoring to support FES control and the independent evaluation and support of walking movements.
Focus Area 1: Gait Abnormality Detection
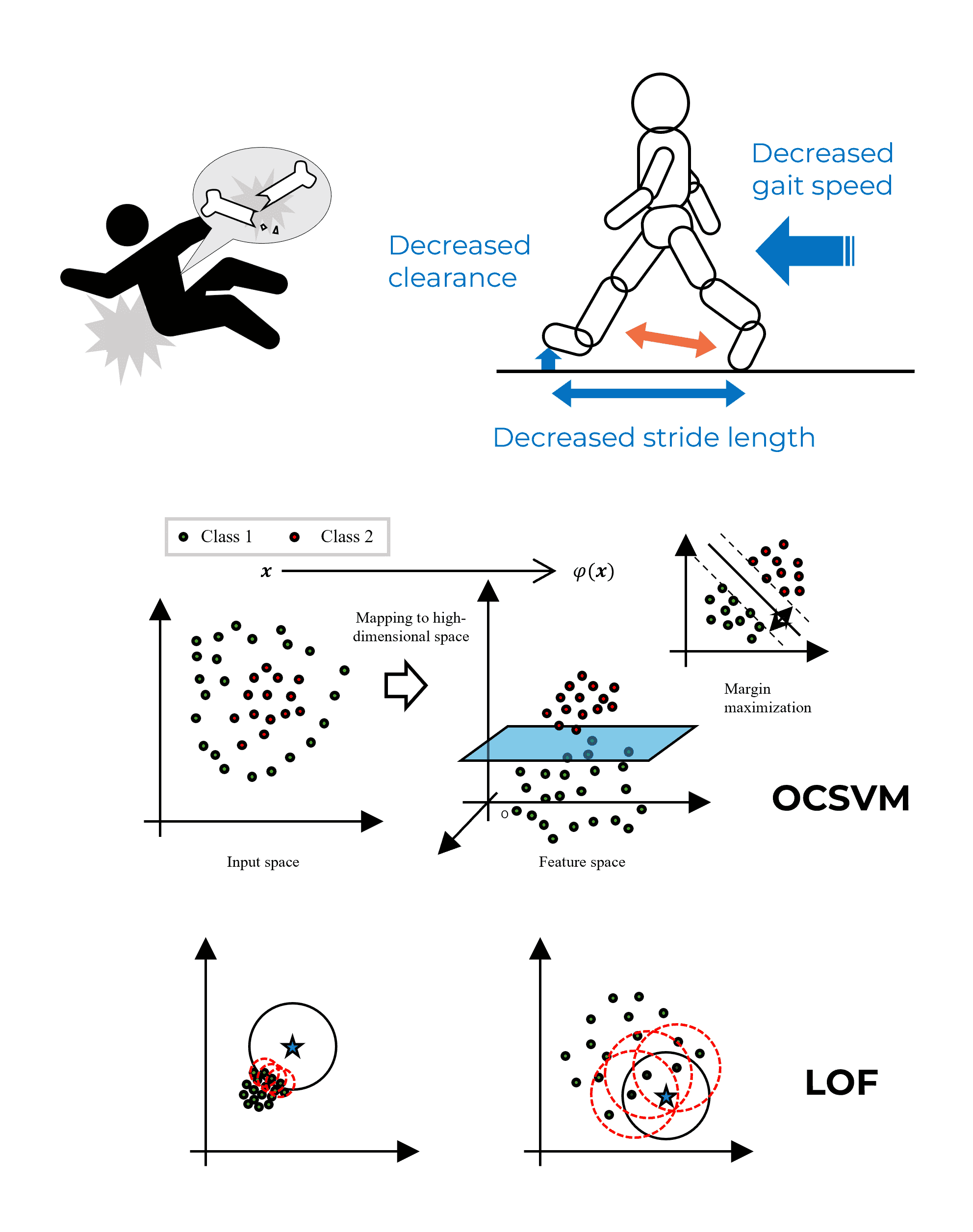
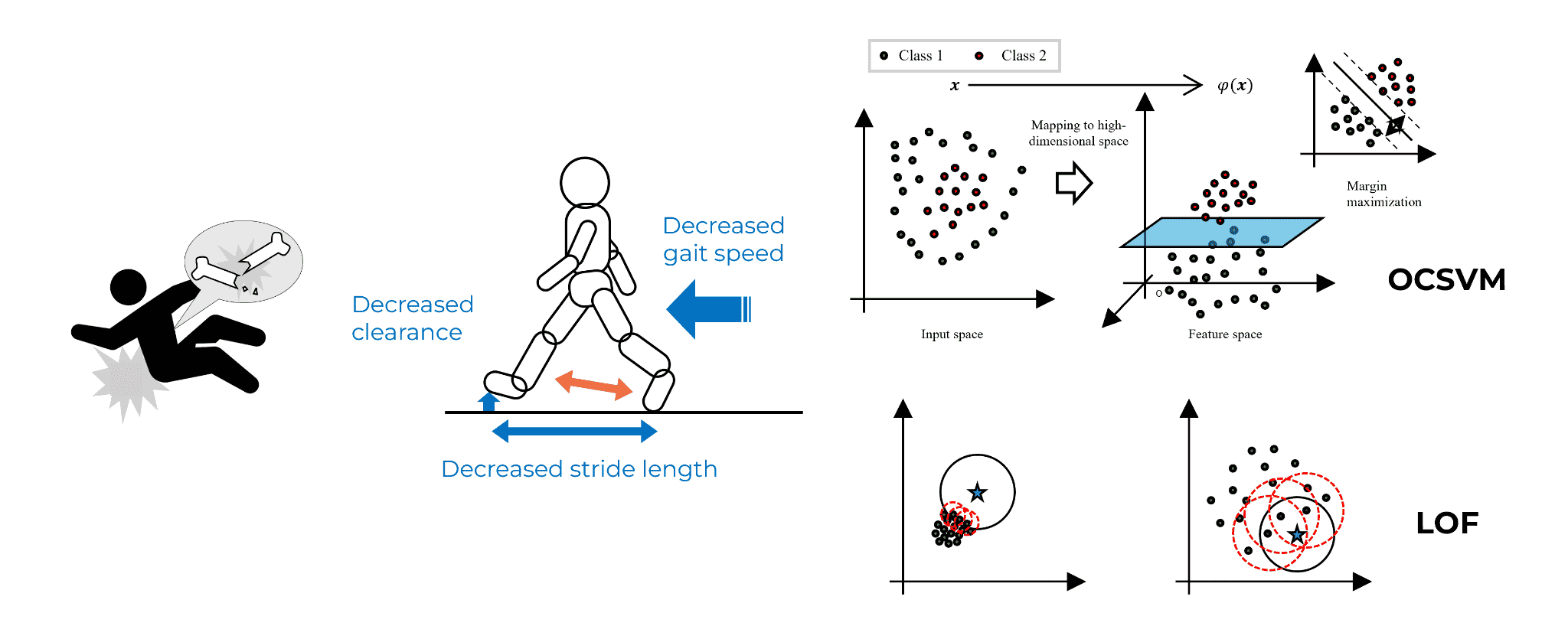
As people age, their sense of balance and muscle strength decline, and those with hemiplegia are at particularly high risk of falling. Walking tests in hospitals are often conducted only once, making it difficult to detect subtle changes in walking patterns in daily life.
In our research, we measure walking in daily life using a small inertial measurement unit (IMU) and use AI to detect differences from “normal walking patterns” for each individual. Since collecting and labeling abnormal data is challenging in traditional supervised learning, we utilize unsupervised learning that relies solely on normal walking data.
Additionally, to make AI judgments more understandable in clinical settings, we have implemented visualizations that highlight which gait metrics or joint angles have changed.
Laboratory Equipment
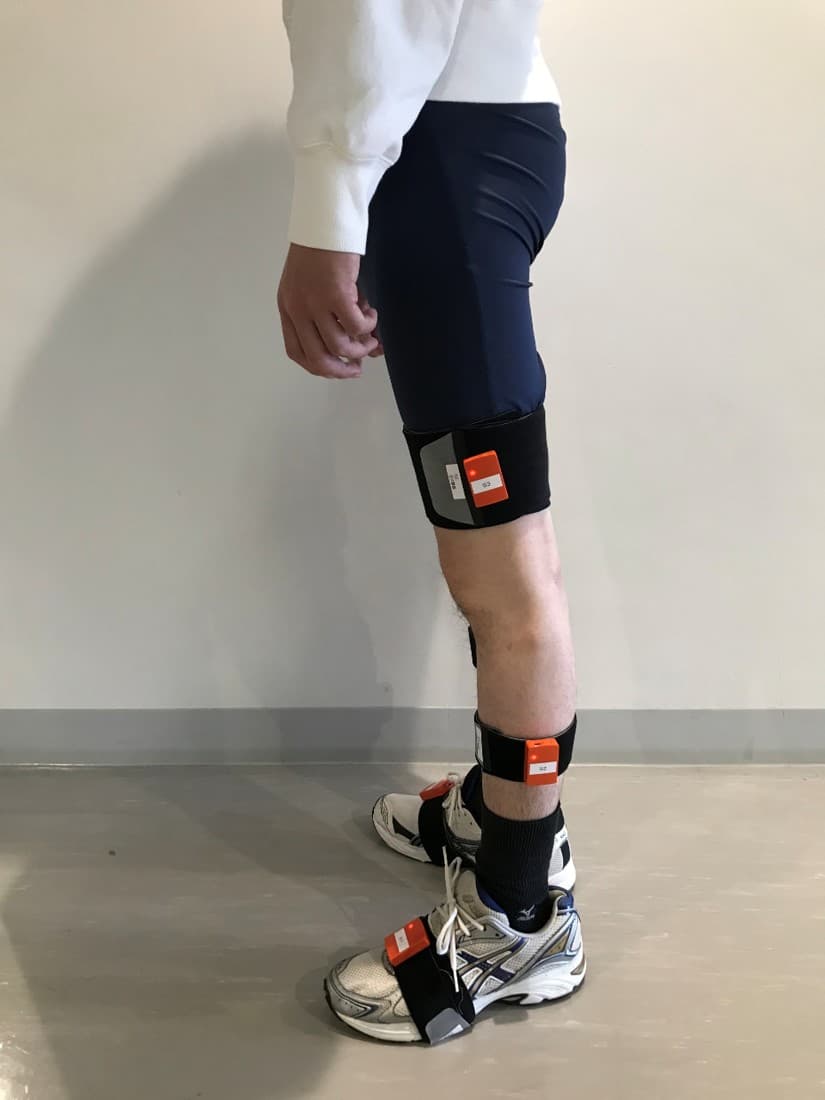 Inertial Measurement Units (IMU)
Wearable sensors capable of measuring acceleration and angular velocity
Inertial Measurement Units (IMU)
Wearable sensors capable of measuring acceleration and angular velocity
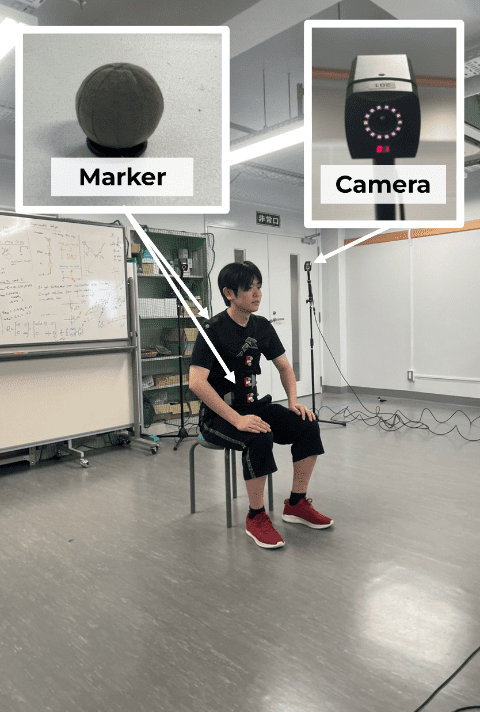 Motion Capture System
Measure 3D movement by tracking attached markers with a camera
Motion Capture System
Measure 3D movement by tracking attached markers with a camera
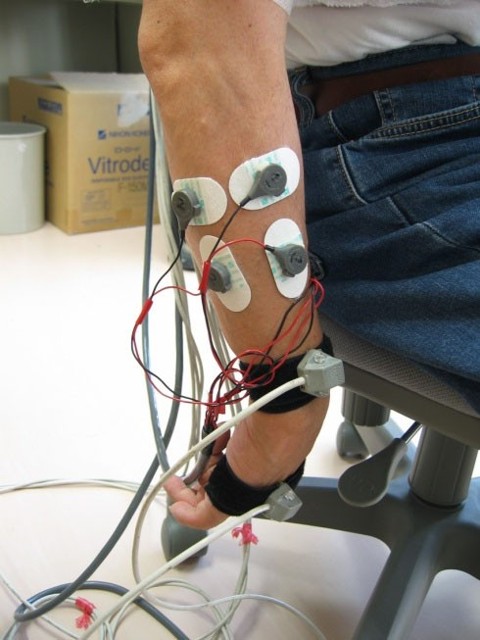 FES System
Apply electrical pulses from electrodes attached to the skin
FES System
Apply electrical pulses from electrodes attached to the skin
 Treadmill
Use for gait assessment
Treadmill
Use for gait assessment
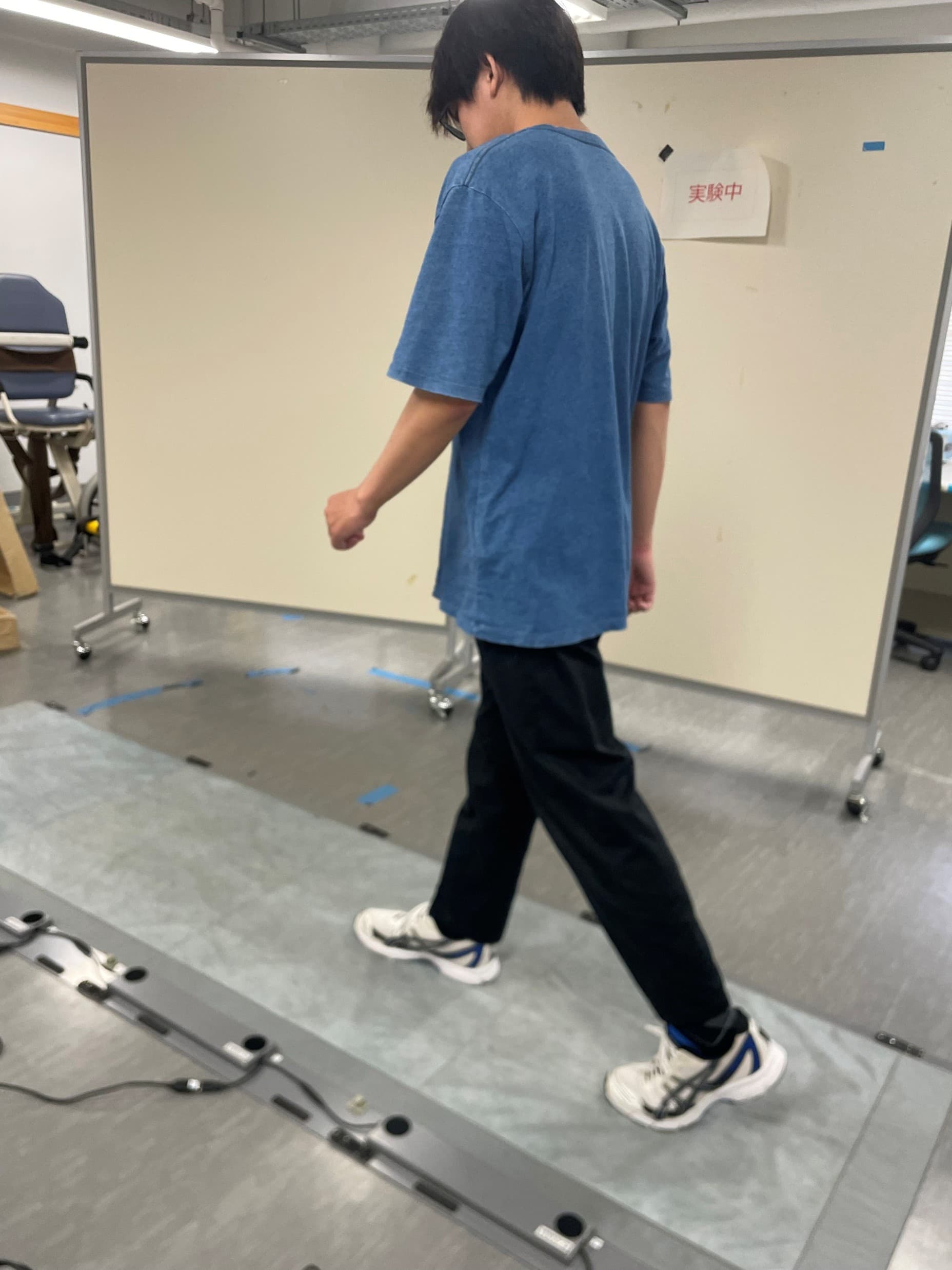 Pressure Sensor
Measure pressure distribution and ground reaction force on the foot
Pressure Sensor
Measure pressure distribution and ground reaction force on the foot
 Personal Computer
Assigned to individuals and used for programming and data analysis
Personal Computer
Assigned to individuals and used for programming and data analysis